Electrical Current That Travels the Length of the Muscle
What is the unstoppable electrical current that travels down the length of the entire surface of a sarcolemma. Muscle tetany typically occurs in response to electrical stimulation at a frequency of 40 Hz to 110 Hz a range in which most household currents exist.
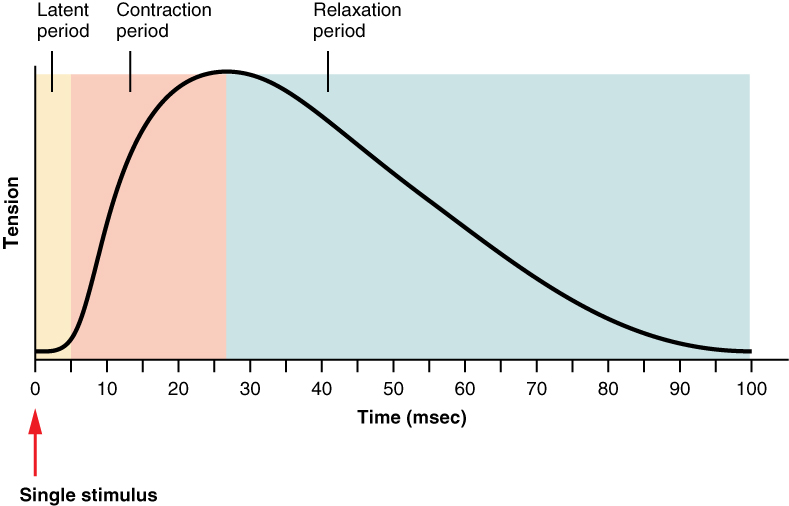
Motor Units And Muscle Twitches
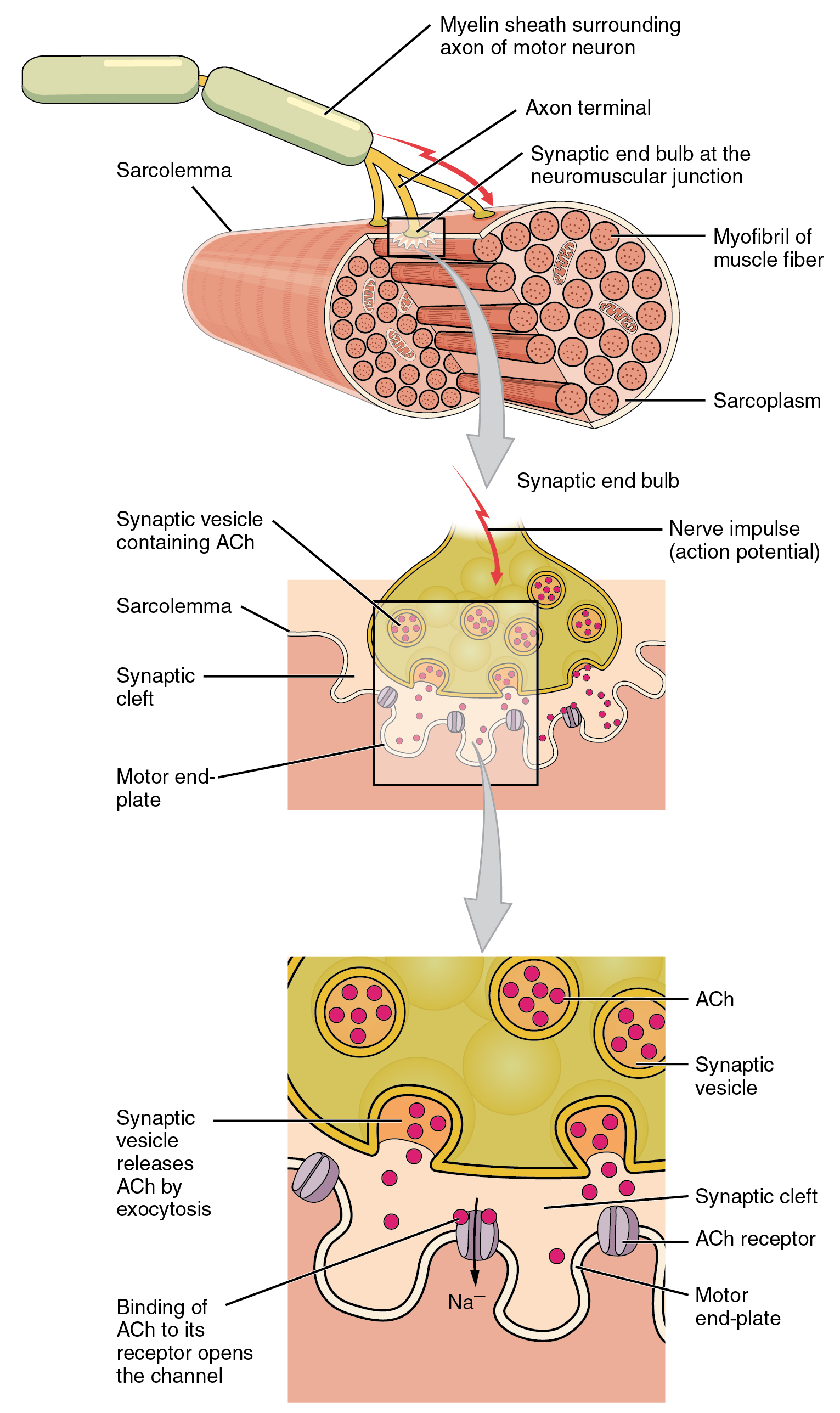
An action potential travels the length of the axon reaching the axon terminals.

. During the healing process the scar tissue has decreased the elasticity and shortened the resting length of the affected muscle to 40 of its normal 100 length. Channels - cardiac muscle cells share many of the same ion channels as neurons and skeletal muscle cells. 1 leak channels - leak K channel 2 voltage-gated Na channels - there is a skeletal muscle voltage-gated Na channel which properties very much like the neuronal voltage-gated Na channel we have already discussed at length.
This problem has been solved. For example the current needed to cause tetanic muscle contractions in the forearm the let-go. The minimum current a human can feel depends on the current type AC or DC and frequency.
Electroporation cell membrane damage is due to the application of a large voltage across a length of tissue. When current flows work measured in watts can be accomplished. Currents above 10 mA can paralyze or freeze muscles.
The neurotransmitters are received by receptors on the other side of the synapse. Each skeletal muscle fiber is controlled by a motor neuron which conducts signals from the brain or spinal cord to the muscle. Cardiac muscle also demonstrates striations the alternating pattern of dark A bands and light I bands attributed to the precise arrangement of the myofilaments and fibrils that are organized in sarcomeres along the length of the cell.
Many of the determinations of electrical current effects in humans were made by Dalziel. Electrical signals called action potentials travel along the neurons axon which branches through the muscle connecting to individual muscle fibers at a neuromuscular junction. The action potential sometimes called a spike is a brief electrical signal or current that occurs in neurons muscle endocrine and plant cells a version can also occur in a bacteria to send a signal to the cilia to move.
Typically the expression is used to describe an injurious exposure to electricity. Electrical current that travels the length of the sarcolemma that results in the contraction of. One neuron and all the skeletal muscles it stimulates is known as a _____.
Electrical current that travels the length of the sarcolemma that results in the contraction of the muscle fiber action potential All of the following proteins are part of the thin filaments except. At this point the axon meets with another neuron muscle or organ at a synapse. Electric current always tries to return to its source that is the transformer or other sources that supplied it.
To understand how a nerve impulse travels the structure of a neuron must be looked at first. The sarcomere itself is bundled within the myofibril that runs the entire length of the muscle fiber and attaches to the sarcolemma at its end. Weve learned that electricity travels in closed circuits through a conductor.
A type of nerve cell that has a specific function to deliver messages to the brain is called a neuron. These messages are nerve impulses and each message is a quick electrical impulse. The sarcomere is the functional unit of the muscle fiber.
The amount of internal current a person can withstand and still be able to control the muscles of the arm and hand can be less than 10 milliamperes milliamps or mA. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume. 10 For any given effect such as tetanic muscle contractions there is a range of current levels that produce the effect due to individual subject differences.
The I band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated by _____. The action potential is transmitted through the synapse by the neurotransmitters. Electric shock occurs upon contact of a human body part with any source of electricity that causes a sufficient current through the skin muscles or hair.
When electric current travels through the T tubule it causes. This is often referred to as the neuron firing. Chemical that enters a muscle cell upon excitation Synaptic cleft Gap between the axon terminals and the plasma membrane of a neighboring muscle cell Action potential Electrical current that travels the length of the sarcolemma that results in the contraction of the muscle fiber Acetylcholinesterase Enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine ACh.
These contractile elements are virtually identical to skeletal muscle. The curren flows for any given voltage depending on the resistace. As myofibrils contract the entire muscle cell contracts.
Phases of action potential-. Now lets take a look at how shock occurs. Effects of electric current.
An electric current is a stream of charged particles such as electrons or ions moving through an electrical conductor or space. If this muscle contraction occurs in the hand contraction of flexors will cause the affected individual to grasp the source and prolong contact with the electrical source. It is the current that determines physiological effects.
For example 110 of an ampere amp of electricity going through the body for just 2 seconds is enough to cause death. When electrical signals passes through dendrites generates action potential. Voltage also known as electric tension si defined as the force that pushes electric current through the body.
TV dramatizations in which electrical shocks are used to bring a heart attack victim out of ventricular fibrillation a massively irregular often. 11 Chemical that enters a muscle cell upon excitation 12 Gap between the axon terminals and the plasma membrane of a neighboring muscle cell 13 Electrical current that travels the length of the muscle 14 Enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine ACh. 10th - 12th grade.
An electrical current can be used to block back pain. The possibility of using electrical current to stimulate muscle action in paralyzed limbs perhaps allowing paraplegics to walk is under study. Action potential is defined as a sudden fast change or coming into action of resting membrane potentialIt travels over long distances and in direction of dendrites to Axon terminal.
Which letter on the graph represents the force generated by this muscle. What is the unstoppable electrical current that travels down the length of the entire surface of a sarcolemma. Electrical current that travels the length of the muscle action potential enzyme that breaks down ACh acetylcholinesterase muscle cells can only directly use the energy in ATP the immediate backup energy source that can directly phosphorylate ADP creatine phosphate the enzyme that phosphorylates creatine creatine kinase.
The sarcoplasmic reticulum stores this chemical action potential electrical current that travels the length of the muscle sodium ions chemical that enters a muscle cell upon excitation acetylcholinesterase enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine synaptic cleft gap between the axon terminals and the plasma membrane of a neighboring muscle cell. 9th - 12th grade. 622 The moving particles are called charge carriers which may be one of several types of particles depending on the conductor.
Neuron communication by electric impulses.

To Carry Out The Functions Of A Muscle Muscle Cells Have Five Characteristics Excitability When Muscle Cells Rece Build Muscle Tissue Types Types Of Muscles

Neuromuscular Junctions And Muscle Contractions Anatomy And Physiology I
0 Response to "Electrical Current That Travels the Length of the Muscle"
Post a Comment